
Introduction
Diffusion models have gained significant attention in the field of artificial intelligence, particularly in generative modeling. These models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in generating high-quality images, audio, and other forms of data. Their success is attributed to their unique ability to refine outputs through a stepwise denoising process. This article delves into the workings of diffusion models, their applications, and their advantages over traditional generative models.
What is a Diffusion Model?
A diffusion model is a type of generative model that learns to generate data by gradually refining random noise. Inspired by thermodynamics, these models simulate a diffusion process where structured data is progressively converted into noise and then reversed to recover meaningful patterns. The training process involves two key stages:
Forward Diffusion Process: This process introduces noise to the data in a systematic manner until the data becomes indistinguishable from pure noise.

Reverse Diffusion Process: The model learns to reverse the noising process, reconstructing high-fidelity samples from random noise using a neural network.
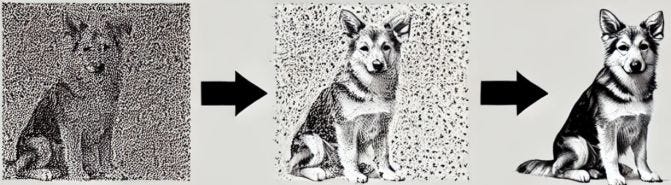
How Diffusion Models Work?
Diffusion models are typically trained using a parameterized function that learns to predict the denoised version of a sample at each step. The steps involved include:
- Noise Addition: Given an original data sample (e.g., image of the dog above), Gaussian noise is incrementally added over multiple steps.
- Learning the Reverse Process: A neural network, often based on U-Net architecture, is trained to predict the denoised output from a noisy input.
- Sampling: Once trained, the model can generate new samples by starting with pure noise and progressively refining it through the learned denoising process.
Applications of Diffusion Models
Diffusion models have been successfully applied in various domains, including:
- Image Generation: Models like DALL·E 2 and Stable Diffusion have shown outstanding results in generating realistic images from text prompts.
- Audio Synthesis: These models can generate high-quality speech and music by refining noisy waveforms.
- Video Generation: Diffusion models can be extended to generate coherent video frames by leveraging sequential denoising.
- Medical Imaging: Used for generating and enhancing medical scans, aiding in diagnosis and research.
- Data Augmentation: Useful for improving machine learning models by generating additional training data.
Advantages of Diffusion Models
Compared to other generative models such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), diffusion models offer several advantages:
- High-Quality Outputs: They produce more detailed and realistic images with fewer artifacts.
- Stable Training: Unlike GANs, which suffer from mode collapse and training instability, diffusion models are easier to train.
- Versatility: They can generate a wide range of data types and adapt to various tasks with minimal modifications.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite their success, diffusion models also have some limitations:
- Computational Complexity: They require significant computational resources due to their iterative sampling process.
- Slow Inference Speed: Generating samples can be slow compared to GANs. Researchers are actively working on improving the efficiency of diffusion models, with innovations such as faster sampling techniques and hybrid architectures.
Conclusion
Diffusion models have emerged as a powerful tool in generative modeling, offering superior output quality and stability over traditional methods. As advancements continue, they are expected to revolutionize various AI-driven applications, from creative content generation to scientific research. Their potential is vast, making them an exciting area of study and development in the field of artificial intelligence.
Leave a comment